Mercedes-Benz E-Class: A Mixed Performance in IIHS Crash Testing
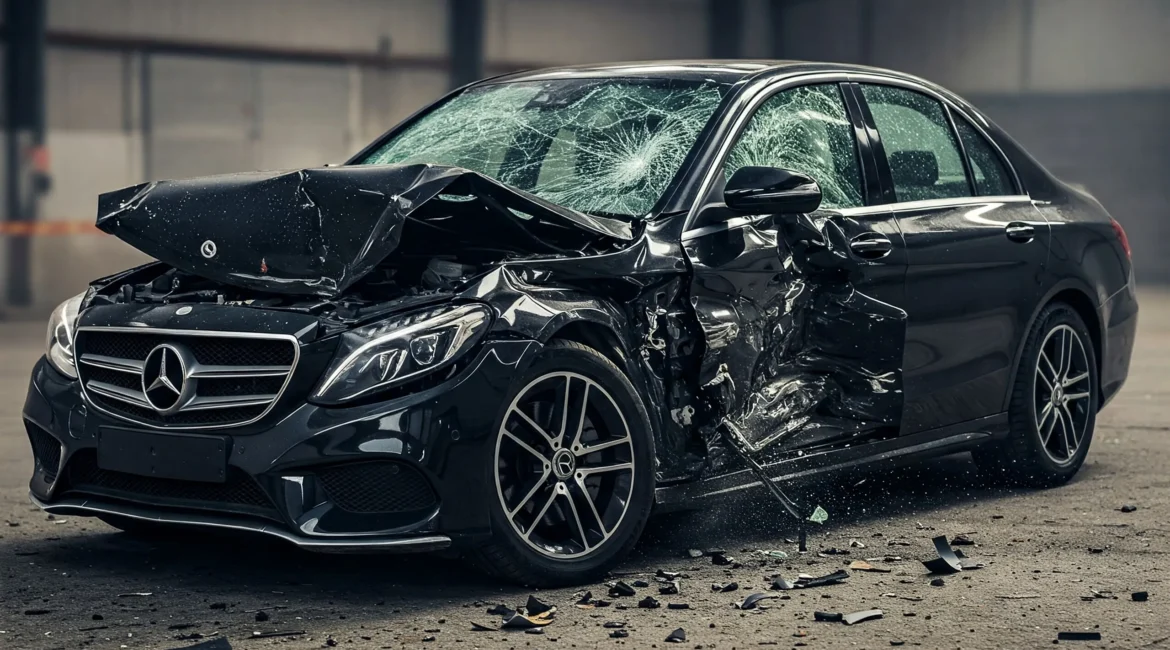
The Mercedes-Benz E-Class, a luxury sedan renowned for its safety features, has shown a mixed performance in recent crash tests conducted by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS). While it excelled in various safety evaluations, it fell short in specific tests, raising questions about its overall safety profile.
Core Findings:
- Moderate Overlap Front Crash Test: The 2025 Mercedes-Benz E-Class received a Marginal rating, primarily due to concerns over its rear passenger restraint system, including shoulder belt positioning and lap belt movement.
- Comparison with Other Models: In contrast, the 2025 Toyota Camry earned a Good rating in the same test, showcasing its impressive safety structure and well-positioned seatbelts, keeping rear passengers well-protected.
Contextualizing Safety Performance
The E-Class’s performance in IIHS tests contrasts with its stellar performance in Euro NCAP evaluations, where it was named the “Best Performer” of 2024. The Euro NCAP tests include full-width frontal, frontal offset, side barrier, side pole, and rear impact scenarios, in which the E-Class demonstrated excellent protection for occupants and vulnerable road users.
Key Safety Features and Evaluations:
- Active Safety Features: The E-Class is equipped with standard Active Brake Assist, which performed well in preventing crashes and injuries to pedestrians, cyclists, and motorcyclists.
- Crashworthiness: The vehicle showed limited injury measures in various crash tests, although there were slight risks of leg injuries in offset-type crashes and chest injuries in full-width frontal crashes for specific dummies.
- Pedestrian and Cyclist Protection: The E-Class provided good head protection for pedestrians, although there were concerns about pelvis and leg injuries. It scored 28.1 out of 36 points for impact protection, a better score than any other similarly priced four-door tested last year.
Statistical Data and Comparative Analysis:
- Euro NCAP vs. IIHS: The difference in ratings between Euro NCAP and IIHS highlights the varying methodologies and focus areas of these testing agencies. Euro NCAP places significant emphasis on active safety features and pedestrian protection, while IIHS focuses on crashworthiness and crash avoidance technologies.
- Comparative Safety Performance: The E-Class’s performance in IIHS tests, particularly in the moderate overlap front crash test, suggests that while it excels in many safety aspects, there are areas for improvement, especially in rear passenger protection.
Recent Developments and Nuanced Perspectives:
- Regulatory Changes: The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has mandated automatic emergency braking (AEB) for all new vehicles starting from 2029, underscoring the importance of active safety features in preventing crashes and saving lives.
- Market Comparisons: The mixed performance of the E-Class in IIHS tests, compared to its excellent performance in Euro NCAP evaluations, underscores the need for comprehensive safety assessments that consider both crashworthiness and active safety features.
Expanding on Safety Evaluations:
- Comprehensive Safety Assessments: The disparity in safety ratings between Euro NCAP and IIHS emphasizes the importance of considering multiple testing frameworks when evaluating a vehicle’s safety.
- Technological Advancements: The integration of advanced safety features, such as AEB and improved restraint systems, is crucial for enhancing vehicle safety and reducing the risk of injuries and fatalities.